Uvod
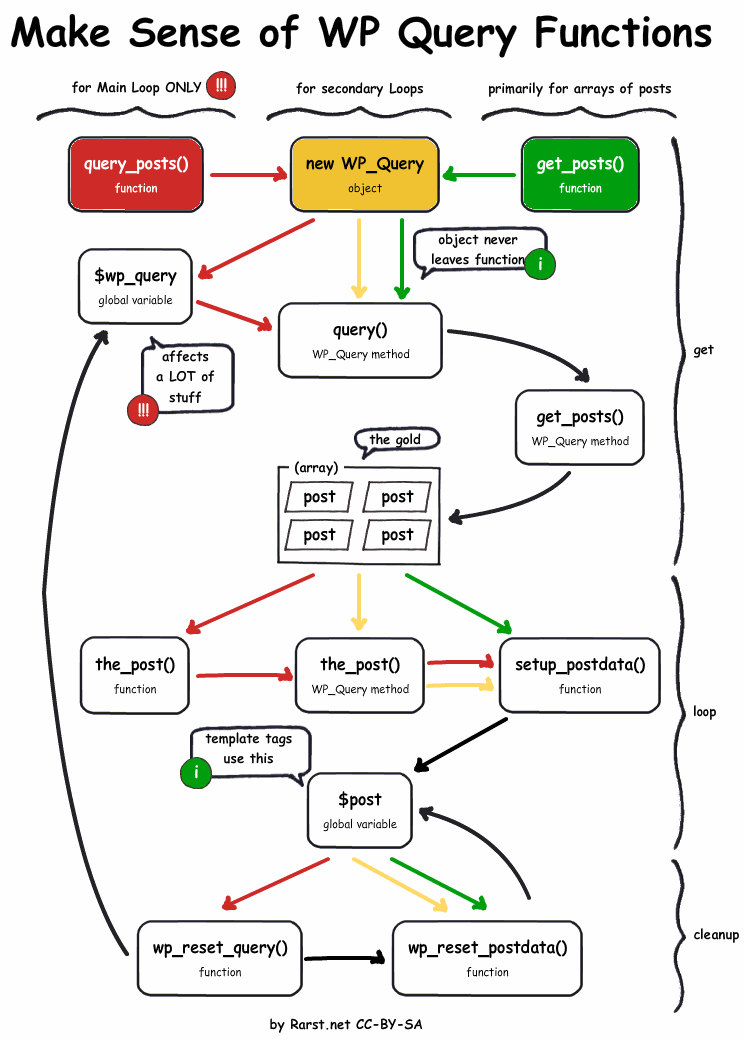
WordPress upiti ka bazi omogućavaju da se kroz mehanizam WordpPress loop-a prikupe podaci i prikažu na stranici. WP_Query je klasa koja stoji iza svih upita ka bazi, a $wp_query je default-ni objekat, i u njemu se čuvaju rezultati upita iz MySQL baze.
Upiti u WordPress-u mogu da se upute i preko funkcija query_posts() i get_posts() koje se takodje zasnivaju na objektu $wp_query. Ali je preporuka da se ipak koristi objekat $wp_query() kao najbolje rešenje, mada takodje može biti prihvatljivo koristiti query_posts() funkciju, dok treba izbegavati funkciju get_posts()!
Ukoliko se menja standardni loop tj. ako se koristio neki custom upit neophodno je po završetku loop-a povratiti prvobitnu defaultnu globalnu $post promenljivu. Ovo se postiže sa funkcijom wp_reset_postdata() postavljenom na mestu gde prestaje petlja tj. odmah iza endwhile.
Za bolje razumevanje prethodno objašnjenih pojmova proučite sliku pored.
Primeri korišćenja različitih vrsta upita
- Upiti na osnovu klase WP_Query
1234567891011121314151617181920<?php// The Query$args= array( 'cat' => 4 );$spec_upit = new WP_Query( $args );// The Loopif ( $spec_upit->have_posts() ) {echo '<ul>';while ( $spec_upit->have_posts() ) {$spec_upit->the_post();echo '<li>' . get_the_title() . '</li>';}echo '</ul>';} else {?><p><?php _e('Sorry, no posts matched your criteria.'); ?></p><?php}/* Restore original Post Data */wp_reset_postdata();?> - Koristeći predefinisane funkcije:
- query_posts()
123456<?php query_posts('posts_per_page=1&category_name=obavjestenje ');if ( have_posts() ) : while ( have_posts() ) : the_post(); ?><a href="<?php the_permalink();?>"><?php the_title(); ><?php endwhile;endif;wp_reset_query(); ?> - get_posts()
123456789101112<?php$posts= get_posts(array('numberposts' => 5,'category' => 2));foreach ($posts as $ post) :setup_postdata($post);?><h1><?php the_title(); ?></h1><?php the_excerpt(); ?><?php endforeach; ?><?php wp_reset_postdata(); ?>
- query_posts()
WP_Query
Opšte principi korišćenja
Parametri objekta WP-Query omogućavaju da se naprave specifični upiti ka bazi. Objekat $wp_query ima ugradjene mnoge metode ali ipak najčešće korišćene su:
-
$wp_query->have_posts()
Koristi se u loop-u ili ispred njega i proverava da li trenutni WP upit ka bazi ima neki razultat tj. da li $wp_query objekat ima vrednost. To je boolean funkcija koja vraća TRUE ili FALSE. Notacija $wp_query->have_posts() u standardnom loop-u je have_posts()
-
$wp_query->the_post()
Ova metoda dohvata sledeći post, i pravi dostupnim globalnu $post promenjivu unutar petlje i sve što ta globalna promenjiva daje:
- $post–>ID – ID of the current post.
- $post–>post_category – Retrieves the ID of the post category.
- $post–>post_parent – ID of the page parent. Useful for creating custom navigational elements.
- $post–>post_title – Post Title
- $post–>post_excerpt – Post excerpt
- $post–>post_content – Retrieves all of the post content, along with any markup.
- $post–>post_name – Retrieving the slug of a post.
- $post–>guid – Post Url
- $post–>post_author – ID of post author post_parent
- $post–>post_type – Returns the type, page or post.
- $post–>menu_order – Returns the menu order as set in the post/page editing window. Often menu items are sorted via this value.
- $post–>post_date – Retrieves the integer timestamp for when the post was published. The output can be customized.
- $post–>post_modified – Retrieves the integer timestamp for when the post was last modified.
- $post–>post_status – Retrieves one of five possible posts statuses: publish, private, draft, pending, future.
- $post–>comment_count – Returns the number of comments, pings, and trackbacks for a given post.
Metode objekta WP_Query
- init() Initialise the object, set all properties to null, zero or false.
- parse_query( $query ) Takes a query string defining the request, parses it and populates all properties apart from $posts, $post_count, $post and
$current_post. - parse_query_vars() Reparse the old query string.
- get( $query_var ) Get a named query variable.
- set( $query_var, $value ) Set a named query variable to a specific value.
- &get_posts() Fetch and return the requested posts from the database. Also populate $posts and $post_count.
- next_post() (to be used when in The Loop) Advance onto the next post in $posts. Increment $current_post and set $post to the (new) current post object (note:
this does not set the global $post variable, only the WP_Query object’s instance variable.) Returns the current post object (This is deprecated pleases use ‘next_post_link()’ ) - the_post() (to be used when in The Loop) Advance onto the next post, and set the global $post variable.
- have_posts() (to be used when in The Loop, or just before The Loop) Determine if we have posts remaining to be displayed. Calls rewind_posts() and returns
false if don’t have posts remaining. Because of the rewind, you can’t rely on have_posts() staying false. See have_posts() note. - rewind_posts() Reset $current_post and $post.
- &query( $query ) Call parse_query() and get_posts(). Return the results of get_posts().
- get_queried_object() Set $queried_object if it’s not already set and return it.
- get_queried_object_id() Set $queried_object_id if it’s not already set and return it.
- WP_Query( $query = ” ) (constructor) If you provide a query string, call query() with it.
Promenjive WP_Query objekta su:
- $query – Holds the query string that was passed to the $wp_query object by WP class.
- $query_vars-An associative array containing the dissected $query: an array of the query variables and their respective values.
- $queried_object-Applicable if the request is a category, author, permalink or Page. Holds information on the requested category, author, post or Page.
- $queried_object_id-If the request is a category, author, permalink or post / page, holds the corresponding ID.
- $posts-Gets filled with the requested posts from the database.
- $post_count-The number of posts being displayed.
- $found_posts-The total number of posts found matching the current query parameters
- $max_num_pages-the total number of pages. Is the result of $found_posts / $posts_per_page
- $current_post-(available during The Loop) Index of the post currently being displayed.
- $post-(available during The Loop) The post currently being displayed.
- $post–>ID – ID of the current post.
- $post–>post_category – Retrieves the ID of the post category.
- $post–>post_parent – ID of the page parent. Useful for creating custom navigational elements.
- $post–>post_title – Post Title
- $post–>post_excerpt – Post excerpt
- $post–>post_content – Retrieves all of the post content, along with any markup.
- $post–>post_name – Retrieving the slug of a post.
- $post–>guid – Post Url
- $post–>post_author – ID of post author post_parent
- $post–>post_type – Returns the type, page or post.
- $post–>menu_order – Returns the menu order as set in the post/page editing window. Often menu items are sorted via this value.
- $post–>post_date – Retrieves the integer timestamp for when the post was published. The output can be customized.
- $post–>post_modified – Retrieves the integer timestamp for when the post was last modified.
- $post–>post_status – Retrieves one of five possible posts statuses: publish, private, draft, pending, future.
- $post–>comment_count – Returns the number of comments, pings, and trackbacks for a given post.
- $is_single
- $is_page
- $is_archive
- $is_preview
- $is_date
- $is_year
- $is_month
- $is_time
- $is_author
- $is_category
- $is_tag
- $is_tax
- $is_search
- $is_feed
- $is_comment_feed
- $is_trackback
- $is_home
- $is_404
- $is_comments_popup
- $is_admin
- $is_attachment
- $is_singular
- $is_robots
- $is_posts_page
- $is_paged
Parametri objekta WP_Query
-
Author
- author(int) – use author id.
- author_name(string) – use ‘user_nicename’ – NOT name.
- author__in(array) .
- author__not_in(array) .
Primeri:
Show Posts for one Author
Display posts by author, using author id:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'author' => 123 ) );Display posts by author, using author ‘user_nicename’:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'author_name' => 'rami' ) );Show Posts From Several Authors
Display posts from several specific authors:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'author' => '2,6,17,38' ) );Exclude Posts Belonging to an Author
Display all posts except those from an author(singular) by prefixing its id with a ‘-‘ (minus) sign:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'author' => -12 ) );Multiple Author Handling
Display posts from multiple authors:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'author__in' => array( 2, 6 ) ) );You can also exclude multiple author this way:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'author__not_in' => array( 2, 6 ) ) ); -
Category
- cat(int) – use category id.
- category_name(string) – use category slug.
- category__and(array) – use category id.
- category__in(array) – use category id.
- category__not_in(array) – use category id.
Show Posts for One Category
Display posts that have this category (and any children of that category), using category id:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'cat' => 4 ) );Display posts that have this category (and any children of that category), using category slug:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'category_name' => 'staff' ) );Display posts that have this category (not children of that category), using category id:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'category__in' => 4 ) );Show Posts From Several Categories
Display posts that have these categories, using category id:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'cat' => '2,6,17,38' ) );Display posts that have these categories, using category slug:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'category_name' => 'staff,news' ) );Display posts that have “all” of these categories:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'category_name' => 'staff+news' ) );Exclude Posts Belonging to Category
Display all posts except those from a category by prefixing its id with a ‘-‘ (minus) sign.
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'cat' => '-12,-34,-56' ) );Multiple Category Handling
Display posts that are in multiple categories. This shows posts that are in both categories 2 and 6:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'category__and' => array( 2, 6 ) ) );To display posts from either category 2 OR 6, you could use cat as mentioned above, or by using category__in (note this does not show posts from any children of these categories):
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'category__in' => array( 2, 6 ) ) );You can also exclude multiple categories this way:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'category__not_in' => array( 2, 6 ) ) ); -
Tag
- tag(string) – use tag slug.
- tag_id(int) – use tag id.
- tag__and(array) – use tag ids.
- tag__in(array) – use tag ids.
- tag__not_in(array) – use tag ids.
- tag_slug__and(array) – use tag slugs.
- tag_slug__in(array) – use tag slugs.
Show Posts for One Tag
Display posts that have this tag, using tag slug:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'tag' => 'cooking' ) );Display posts that have this tag, using tag id:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'tag_id' => 13 ) );Show Posts From Several Tags
Display posts that have “either” of these tags:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'tag' => 'bread,baking' ) );Display posts that have “all” of these tags:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'tag' => 'bread+baking+recipe' ) );Multiple Tag Handling
Display posts that are tagged with both tag id 37 and tag id 47:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'tag__and' => array( 37, 47 ) ) );To display posts from either tag id 37 or 47, you could use tag as mentioned above, or explicitly specify by using tag__in:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'tag__in' => array( 37, 47 ) ) );Display posts that do not have any of the two tag ids 37 and 47:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'tag__not_in' => array( 37, 47 ) ) );The tag_slug__in and tag_slug__and behave much the same, except match against the tag’s slug.
-
Taxonomy
- {tax}(string) – use taxonomy slug. (Deprecatedsince Version 3.1 in favor of ‘tax_query’).
- tax_query(array) – use taxonomy parameters (available since Version 3.1).
- relation(string) – The logical relationship between each inner taxonomy array when there is more than one. Possible values are ‘AND’, ‘OR’. Do
not use with a single inner taxonomy array.- taxonomy(string) – Taxonomy.
- field(string) – Select taxonomy term by. Possible values are ‘term_id’, ‘name’ and ‘slug’. Default value is ‘term_id’.
- terms(int/string/array) – Taxonomy term(s).
- include_children(boolean) – Whether or not to include children for hierarchical taxonomies. Defaults to true.
- operator(string) – Operator to test. Possible values are ‘IN’, ‘NOT IN’, ‘AND’, ‘EXISTS’ and ‘NOT EXISTS’. Default value is ‘IN’.
- relation(string) – The logical relationship between each inner taxonomy array when there is more than one. Possible values are ‘AND’, ‘OR’. Do
Simple Taxonomy Query:
Display posts tagged with bob, under people custom taxonomy:
1234567891011$args = array('post_type' => 'post','tax_query' => array(array('taxonomy' => 'people','field' => 'slug','terms' => 'bob',),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Multiple Taxonomy Handling:
Display posts from several custom taxonomies:
123456789101112131415161718$args = array('post_type' => 'post','tax_query' => array('relation' => 'AND',array('taxonomy' => 'movie_genre','field' => 'slug','terms' => array( 'action', 'comedy' ),),array('taxonomy' => 'actor','field' => 'term_id','terms' => array( 103, 115, 206 ),'operator' => 'NOT IN',),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Display posts that are in the quotes category OR have the quote <a href=”/Post_Formats” title=”Post Formats”>format</a>:
1234567891011121314151617$args = array('post_type' => 'post','tax_query' => array('relation' => 'OR',array('taxonomy' => 'category','field' => 'slug','terms' => array( 'quotes' ),),array('taxonomy' => 'post_format','field' => 'slug','terms' => array( 'post-format-quote' ),),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Nested Taxonomy Handling:
The ‘tax_query’ clauses can be nested, to create more complex queries. Example: Display posts that are in the quotes category OR both have the quote post format AND are in the wisdom category:
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425$args = array('post_type' => 'post','tax_query' => array('relation' => 'OR',array('taxonomy' => 'category','field' => 'slug','terms' => array( 'quotes' ),),array('relation' => 'AND',array('taxonomy' => 'post_format','field' => 'slug','terms' => array( 'post-format-quote' ),),array('taxonomy' => 'category','field' => 'slug','terms' => array( 'wisdom' ),),),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args ); -
Post & Page
- p(int) – use post id.
- name(string) – use post slug.
- page_id(int) – use page id.
- pagename(string) – use page slug.
- post_parent(int) – use page id to return only child pages. Set to 0 to return only top-level entries.
- post_parent__in(array) – use post ids. Specify posts whose parent is in an array. (available since Version 3.6)
- post_parent__not_in(array) – use post ids. Specify posts whose parent is not in an array. (available since Version 3.6)
- post__in(array) – use post ids. Specify posts to retrieve. ATTENTIONIf you use sticky posts, they will be included (prepended!) in the posts
you retrieve whether you want it or not. To suppress this behaviour use ignore_sticky_posts. - post__not_in(array) – use post ids. Specify post NOT to retrieve.
- post_name__in(array) – use post slugs. Specify posts to retrieve. (Will be available in Version 4.4)
Show Post/Page by ID
Display post by ID:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'p' => 7 ) );Display page by ID:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'page_id' => 7 ) );Show Post/Page by Slug
Display post by slug:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'name' => 'about-my-life' ) );Display page by slug:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'pagename' => 'contact' ) );Show Child Posts/Pages
Display child page using the slug of the parent and the child page, separated by a slash (e.g. ‘parent_slug/child_slug’):
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'pagename' => 'contact_us/canada' ) );Display child pages using parent page ID:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post_parent' => 93 ) );Display only top-level pages, exclude all child pages:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post_parent' => 0 ) );Display posts whose parent is in an array:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post_parent__in' => array( 2, 5, 12, 14, 20 ) ) );Multiple Posts/Pages Handling
Display only the specific posts:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post_type' => 'page', 'post__in' => array( 2, 5, 12, 14, 20 ) ) );Display all posts but NOT the specified ones:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post_type' => 'post', 'post__not_in' => array( 2, 5, 12, 14, 20 ) ) );Note: you cannot combine post__in and post__not_in in the same query.
Also note that using a string containing a comma separated list will not work here. If you’re passing a variable, make sure it’s a proper array of integer values:
1234567// This will NOT work$exclude_ids = '1,2,3';$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post__not_in' => array( $exclude_ids ) ) );// This WILL work$exclude_ids = array( 1, 2, 3 );$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post__not_in' => $exclude_ids ) ); -
Pasword
- has_password(bool) – true for posts with passwords ; false for posts without passwords ; null for all posts with and without passwords
(available since Version 3.9). - post_password(string) – show posts with a particular password (available since Version 3.9)
Show Posts with/without passwords
Display only password protected posts:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'has_password' => true ) );Display only posts without passwords:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'has_password' => false ) );Display only posts with and without passwords:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'has_password' => null ) );Show Posts with particular password
Display posts with ‘zxcvbn’ password:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post_password' => 'zxcvbn' ) ); - has_password(bool) – true for posts with passwords ; false for posts without passwords ; null for all posts with and without passwords
-
Type
post_type(string / array) – use post types. Retrieves posts by Post Types, default value is ‘post’. If ‘tax_query’ is set for a
query, the default value becomes ‘any’;- ‘post’ – a post.
- ‘page’ – a page.
- ‘revision’ – a revision.
- ‘attachment’ – an attachment. Whilst the default WP_Query post_status is ‘publish’, attachments have a default post_status of ‘inherit’. This
means no attachments will be returned unless you also explicitly set post_status to ‘inherit’ or ‘any’. (See post_status, below) - ‘nav_menu_item’ – a navigation menu item
- ‘any’ – retrieves any type except revisions and types with ‘exclude_from_search’ set to true.
- Custom Post Types (e.g. movies)
Show Post by Type
Display only pages:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post_type' => 'page' ) );Display ‘any’ post type (retrieves any type except revisions and types with ‘exclude_from_search’ set to TRUE):
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post_type' => 'any' ) );Display multiple post types, including custom post types:
1234$args = array('post_type' => array( 'post', 'page', 'movie', 'book' ));$query = new WP_Query( $args ); -
Status
post_status(string / array) – use post status. Retrieves posts by Post Status. Default value is ‘publish’, but if the user is logged
in, ‘private’ is added. And if the query is run in an admin context (administration area or AJAX call), protected statuses are added too. By default protected
statuses are ‘future’, ‘draft’ and ‘pending’.- ‘publish’ – a published post or page.
- ‘pending’ – post is pending review.
- ‘draft’ – a post in draft status.
- ‘auto-draft’ – a newly created post, with no content.
- ‘future’ – a post to publish in the future.
- ‘private’ – not visible to users who are not logged in.
- ‘inherit’ – a revision. see get_children.
- ‘trash’ – post is in trashbin (available since Version 2.9).
- ‘any’ – retrieves any status except those from post statuses with ‘exclude_from_search’ set to true (i.e. trash and auto-draft).
Show Post by Status
Display only drafts:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post_status' => 'draft' ) );Display multiple post status:
1234$args = array('post_status' => array( 'pending', 'draft', 'future' ));$query = new WP_Query( $args );Display all attachments:
12345$args = array('post_status' => 'any','post_type' => 'attachment');$query = new WP_Query( $args ); -
Pagination
- nopaging(boolean) – show all posts or use pagination. Default value is ‘false’, use paging.
- posts_per_page(int) – number of post to show per page (available since Version 2.1, replaced showpostsparameter). Defaults to the value specified in the reading settings for the number of posts to list.Use ‘posts_per_page’=>-1
to show all posts (the ‘offset’ parameter is ignored with a -1 value). Set the ‘paged’ parameter if pagination is off after using this parameter.
Note: if the query is in a feed, wordpress overwrites this parameter with the stored ‘posts_per_rss’ option. To reimpose the limit, try using the ‘post_limits’ filter,
or filter ‘pre_option_posts_per_rss’ and return -1 - posts_per_archive_page(int) – number of posts to show per page – on archive pages only. Over-rides posts_per_pageand showposts
on pages where is_archive() or is_search() would be true. - offset(int) – number of post to displace or pass over. Warning: Setting the offset parameter overrides/ignores the paged parameter and
breaks pagination (Click here for a workaround). The ‘offset’ parameter is ignored when ‘posts_per_page’=>-1 (show all posts) is used. - paged(int) – number of page. Show the posts that would normally show up just on page X when using the “Older Entries” link.
- page(int) – number of page for a static front page. Show the posts that would normally show up just on page X of a Static Front Page.
- ignore_sticky_posts(boolean) – ignore post stickiness (available since Version 3.1, replaced caller_get_postsparameter).
false (default): move sticky posts to the start of the set. true: do not move sticky posts to the start of the set.
Show x Posts per page
Display 3 posts per page:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'posts_per_page' => 3 ) );Show All Post
Display all posts in one page:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'posts_per_page' => -1 ) );Display all posts by disabling pagination:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'nopaging' => true ) );Pass over Posts
Display posts from the 4th one:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'offset' => 3 ) );Display 5 posts per page which follow the 3 most recent posts:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'posts_per_page' => 5, 'offset' => 3 ) );Show Posts from page x
Display posts from page number 6:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'paged' => 6 ) );Show Posts from Current Page
Display posts from current page:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'paged' => get_query_var( 'paged' ) ) );Display posts from the current page and set the ‘paged’ parameter to 1 when the query variable is not set (first page).
12$paged = ( get_query_var('paged') ) ? get_query_var('paged') : 1;$query = new WP_Query( array( 'paged' => $paged ) );Pagination Note: Use get_query_var(‘page’); if you want your query to work in a Page template that you’ve set as your static front page. The query variable ‘page’ also holds the pagenumber for a single paginated Post or Page that includes the <!--nextpage--> Quicktag in the post content.
Display posts from current page on a static front page:
12$paged = ( get_query_var('page') ) ? get_query_var('page') : 1;$query = new WP_Query( array( 'paged' => $paged ) );Show Sticky Posts
Display just the first sticky post:
12$sticky = get_option( 'sticky_posts' );$query = new WP_Query( array( 'p' => $sticky[0] ) );Display just the first sticky post, if none return the last post published:
123456$args = array('posts_per_page' => 1,'post__in' => get_option( 'sticky_posts' ),'ignore_sticky_posts' => 1,);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Display just the first sticky post, if none return nothing:
12345678910$sticky = get_option( 'sticky_posts' );$args = array('posts_per_page' => 1,'post__in' => $sticky,'ignore_sticky_posts' => 1,);$query = new WP_Query( $args );if ( $sticky[0] ) {// insert here your stuff...}Don’t Show Sticky Posts
Exclude all sticky posts from the query:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'post__not_in' => get_option( 'sticky_posts' ) ) );Exclude sticky posts from a category. Return ALL posts within the category, but don’t show sticky posts at the top. The ‘sticky posts’ will still show in their natural position (e.g. by date):
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'ignore_sticky_posts' => 1, 'posts_per_page' => 3, 'cat' => 6 );Exclude sticky posts from a category. Return posts within the category, but exclude sticky posts completely, and adhere to paging rules:
123456789$paged = get_query_var( 'paged' ) ? get_query_var( 'paged' ) : 1;$sticky = get_option( 'sticky_posts' );$args = array('cat' => 3,'ignore_sticky_posts' => 1,'post__not_in' => $sticky,'paged' => $paged,);$query = new WP_Query( $args ); -
Order
orderby(string | array) – Sort retrieved posts by parameter. Defaults to ‘date (post_date)’. One or more options can be passed.
orderby(string | array) – Sort retrieved posts by parameter. Defaults to ‘date (post_date)’. One or more options can be passed.- ‘none’ – No order (available since Version 2.8).
- ‘ID’ – Order by post id. Note the capitalization.
- ‘author’ – Order by author.
- ‘title’ – Order by title.
- ‘name’ – Order by post name (post slug).
- ‘type’ – Order by post type (available since Version 4.0).
- ‘date’ – Order by date.
- ‘modified’ – Order by last modified date.
- ‘parent’ – Order by post/page parent id.
- ‘rand’ – Random order.
- ‘comment_count’ – Order by number of comments (available since Version 2.9).
- ‘menu_order’ – Order by Page Order. Used most often for Pages (Order field in the Edit Page Attributes box) and for Attachments (the integer fields in
the Insert / Upload Media Gallery dialog), but could be used for any post type with distinct ‘menu_order’ values (they all default to 0). - ‘meta_value’ – Note that a ‘meta_key=keyname’ must also be present in the query. Note also that the sorting will be alphabetical which is fine for
strings (i.e. words), but can be unexpected for numbers (e.g. 1, 3, 34, 4, 56, 6, etc, rather than 1, 3, 4, 6, 34, 56 as you might naturally expect). Use ‘meta_value_num’
instead for numeric values. You may also specify ‘meta_type’ if you want to cast the meta value as a specific type. Possible values are ‘NUMERIC’, ‘BINARY’,
‘CHAR’, ‘DATE’, ‘DATETIME’, ‘DECIMAL’, ‘SIGNED’, ‘TIME’, ‘UNSIGNED’, same as in ‘$meta_query’. - ‘meta_value_num’ – Order by numeric meta value (available since Version 2.8). Also note that a ‘meta_key=keyname’ must also be present in the query.
This value allows for numerical sorting as noted above in ‘meta_value’. - ‘post__in’ – Preserve post ID order given in the post__in array (available since Version 3.5).
Show Posts sorted by Title, Descending order
Display posts sorted by post ‘title’ in a descending order:
12345$args = array('orderby' => 'title','order' => 'DESC',);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Display posts sorted by ‘menu_order’ with a fallback to post ‘title’, in a descending order:
12345$args = array('orderby' => 'menu_order title','order' => 'DESC',);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Show Random Post
Display one random post:
123456$args = array('orderby' => 'rand','posts_per_page' => '1',);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Show Popular Posts
Display posts ordered by comment count:
1234$args = array('orderby' => 'comment_count');$query = new WP_Query( $args );Show Products sorted by Price
Display posts with ‘Product’ type ordered by ‘Price’ custom field:
123456$args = array('post_type' => 'product','orderby' => 'meta_value_num','meta_key' => 'price',);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Multiple ‘orderby’ values
Display pages ordered by ‘title’ and ‘menu_order’. (title is dominant):
123456$args = array('post_type' => 'page','orderby' => 'title menu_order','order' => 'ASC',);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Multiple ‘orderby’ values using an array
Display pages ordered by ‘title’ and ‘menu_order’ with different sort orders (ASC/DESC) (available since Version 4.0):
1234$args = array('orderby' => array( 'title' => 'DESC', 'menu_order' => 'ASC' ));$query = new WP_Query( $args );Mulitiple orderby/order pairs
12345$args = array('orderby' => array( 'meta_value_num' => 'DESC', 'title' => 'ASC' ),'meta_key' => 'age');$query = new WP_Query( $args );‘orderby’ with ‘meta_value’ and custom post type
Display posts of type ‘my_custom_post_type’, ordered by ‘age’, and filtered to show only ages 3 and 4 (using meta_query).
1234567891011121314$args = array('post_type' => 'my_custom_post_type','meta_key' => 'age','orderby' => 'meta_value_num','order' => 'ASC','meta_query' => array(array('key' => 'age','value' => array( 3, 4 ),'compare' => 'IN',),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args ); -
Date
- year(int) – 4 digit year (e.g. 2011).
- monthnum(int) – Month number (from 1 to 12).
- w(int) – Week of the year (from 0 to 53). Uses MySQL WEEK command. The mode is dependent on the “start_of_week” option.
- day(int) – Day of the month (from 1 to 31).
- hour(int) – Hour (from 0 to 23).
- minute(int) – Minute (from 0 to 60).
- second(int) – Second (0 to 60).
- m(int) – YearMonth (For e.g.: 201307).
- date_query(array) – Date parameters (available since Version 3.7).
Returns posts dated December 12, 2012:
1$query = new WP_Query( 'year=2012&monthnum=12&day=12' );or:
12345678910$args = array('date_query' => array(array('year' => 2012,'month' => 12,'day' => 12,),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Returns posts for today:
12$today = getdate();$query = new WP_Query( 'year=' . $today['year'] . '&monthnum=' . $today['mon'] . '&day=' . $today['mday'] );or:
1234567891011$today = getdate();$args = array('date_query' => array(array('year' => $today['year'],'month' => $today['mon'],'day' => $today['mday'],),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Returns posts for this week:
123$week = date( 'W' );$year = date( 'Y' );$query = new WP_Query( 'year=' . $year . '&w=' . $week );or:
123456789$args = array('date_query' => array(array('year' => date( 'Y' ),'week' => date( 'W' ),),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Return posts between 9AM to 5PM on weekdays
123456789101112131415161718$args = array('date_query' => array(array('hour' => 9,'compare' => '>=',),array('hour' => 17,'compare' => '<=',),array('dayofweek' => array( 2, 6 ),'compare' => 'BETWEEN',),),'posts_per_page' => -1,);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Return posts from January 1st to February 28th
123456789101112131415$args = array('date_query' => array(array('after' => 'January 1st, 2013','before' => array('year' => 2013,'month' => 2,'day' => 28,),'inclusive' => true,),),'posts_per_page' => -1,);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Note that if a strtotime()-compatible string with just a date was passed in the before parameter, this will be converted to 00:00:00 on that date. In this case, even if inclusive was set to true, the date would not be included in the query. If you want a before date to be inclusive, include the time as well, such as ‘before’ => ‘2013-02-28 23:59:59’, or use the array format, which is adjusted automatically if inclusive is set.
Return posts made over a year ago but modified in the past month
1234567891011121314$args = array('date_query' => array(array('column' => 'post_date_gmt','before' => '1 year ago',),array('column' => 'post_modified_gmt','after' => '1 month ago',),),'posts_per_page' => -1,);$query = new WP_Query( $args ); -
Custom Field
- meta_key(string) – Custom field key.
- meta_value(string) – Custom field value.
- meta_value_num(number) – Custom field value.
- meta_compare(string) – Operator to test the ‘meta_value’. Possible values are ‘=’, ‘!=’, ‘>’, ‘>=’, ‘<‘, ‘<=’, ‘LIKE’, ‘NOT
LIKE’, ‘IN’, ‘NOT IN’, ‘BETWEEN’, ‘NOT BETWEEN’, ‘NOT EXISTS’, ‘REGEXP’, ‘NOT REGEXP’ or ‘RLIKE’. Default value is ‘=’.
- meta_query(array) – Custom field parameters (available since Version 3.1).
- relation(string) – The logical relationship between each inner meta_query array when there is more than one. Possible values are ‘AND’, ‘OR’. Do
not use with a single inner meta_query array.
- relation(string) – The logical relationship between each inner meta_query array when there is more than one. Possible values are ‘AND’, ‘OR’. Do
Simple Custom Field Query:
Display posts where the custom field key is ‘color’, regardless of the custom field value:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'meta_key' => 'color' ) );Display posts where the custom field value is ‘blue’, regardless of the custom field key:
1$query = new WP_Query( array( 'meta_value' => 'blue' ) );Display Page where the custom field value is ‘blue’, regardless of the custom field key:
12345$args = array('meta_value' => 'blue','post_type' => 'page');$query = new WP_Query( $args );Display posts where the custom field key is ‘color’ and the custom field value is ‘blue’:
12345$args = array('meta_key' => 'color','meta_value' => 'blue');$query = new WP_Query( $args );Display posts where the custom field key is ‘color’ and the custom field value IS NOT ‘blue’:
123456$args = array('meta_key' => 'color','meta_value' => 'blue','meta_compare' => '!=');$query = new WP_Query( $args );Display posts where the custom field key is a set date and the custom field value is now. Displays only posts which date has not passed.
1234567$args = array('post_type' => 'event','meta_key' => 'event_date','meta_value' => date( "Ymd" ), // change to how "event date" is stored'meta_compare' => '>',);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Display ‘product'(s) where the custom field key is ‘price’ and the custom field value that is LESS THAN OR EQUAL TO 22.
By using the ‘meta_value’ parameter the value 99 will be considered greater than 100 as the data are stored as ‘strings’, not ‘numbers’. For number comparison use ‘meta_value_num’.1234567$args = array('meta_key' => 'price','meta_value' => '22','meta_compare' => '<=','post_type' => 'product');$query = new WP_Query( $args );Display posts with a custom field value of zero (0), regardless of the custom field key:
1234$args = array('meta_value' => '_wp_zero_value');$query = new WP_Query( $args );Single Custom Field Handling:
Display posts from a single custom field:
1234567891011$args = array('post_type' => 'product','meta_query' => array(array('key' => 'color','value' => 'blue','compare' => 'NOT LIKE',),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args );(Note that meta_query expects nested arrays, even if you only have one query.)
Multiple Custom Field Handling:
Display posts from several custom field:
1234567891011121314151617$args = array('post_type' => 'product','meta_query' => array(array('key' => 'color','value' => 'blue','compare' => 'NOT LIKE',),array('key' => 'price','value' => array( 20, 100 ),'type' => 'numeric','compare' => 'BETWEEN',),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args );Display posts that have meta key ‘color’ NOT LIKE value ‘blue’ OR meta key ‘price’ with values BETWEEN 20 and 100:
123456789101112131415161718$args = array('post_type' => 'product','meta_query' => array('relation' => 'OR',array('key' => 'color','value' => 'blue','compare' => 'NOT LIKE',),array('key' => 'price','value' => array( 20, 100 ),'type' => 'numeric','compare' => 'BETWEEN',),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args );The ‘meta_query’ clauses can be nested in order to construct complex queries. For example, show productss where color=orange OR color=red&size=small translates to the following:
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425$args = array('post_type' => 'product','meta_query' => array('relation' => 'OR',array('key' => 'color','value' => 'orange','compare' => '=',),array('relation' => 'AND',array('key' => 'color','value' => 'red','compare' => '=',),array('key' => 'size','value' => 'small','compare' => '=',),),),);$query = new WP_Query( $args );